2.1 前交叉韧带重建术后早期应用神经肌肉电刺激的研究现状
2.1.1 神经肌肉电刺激的功能、作用机制及应用概 况 神经肌肉电刺激疗法(简称NMES)是应用低频脉冲电流刺激肌肉使其收缩,以恢复其运动功能的方法。神经肌肉电刺激为便携式表面电极设备,作用于肌肉可使其产生肉眼可见收缩[1]。已被证实能用于治疗受损肌肉,使用神经肌肉电刺激治疗可保持肌肉蛋白合成[2],防止由于肢体长时间固定制动造成的肌肉萎缩[3]。
早在1964年就有文献报道神经肌肉电刺激能使肌肉产生可见收缩,促进功能恢复[4]。动物实验和临床研究证实[5],神经肌肉电刺激疗法可使肌肉被动地有节律性地收缩,维持肌肉正常功能,延缓失用性萎缩,为神经再支配创造条件,并可促进受损神经修复与再生,恢复其传导功能[6]。
在前交叉韧带损伤重建术后进行股四头肌电刺激,对肌力恢复有利。这是通过易化作用和提高运动单位兴奋性实现的[7]。肌肉大小以及髓鞘形成性能,是运动单位募集引起兴奋性提高的基础[8]。易化作用和提高运动单位兴奋性是电刺激股四头肌对前交叉韧带损伤重建后肌力恢复的生理基础[7]。
神经肌肉电刺激可提高肌力、增加运动范围、减轻水肿、减缓萎缩、促进组织愈合以及缓解疼痛。郑光新等[9]将神经肌肉电刺激应用于全膝置换后股四头肌力量康复训练,结果表明神经肌肉电刺激有助于早期改善伸膝装置的功能。在临床上神经肌肉电刺激广泛应用于治疗脑损伤后引起的肢体瘫痪、吞咽障碍、构音障碍、尿便失禁等康复治疗,也包括应用于治疗周围神经损伤后的康复[10]。
2.1.2 神经肌肉电刺激激频率的选择 根据治疗目标不同,刺激频率有很大差异[11-12]。为避免疲劳和不适,临床常用低频刺激,可使平滑肌收缩保持在低强度水平[13]。
一项研究对比了几种不同的刺激模式和频率,低于16 Hz的刺激强度不足以使股四头肌收缩延长膝盖弯曲角达40°[14]。
Edwards等1982年研究观察到“低频疲劳”现象。效果可持续24 h或更长时间,更高的频率则无此效果。之后Bigland等1979年研究发现对手部肌肉进行较高频电刺激(50-80 Hz)可导致肌力在20 s内迅速下降。
较新研究显示刺激频率与运动单位放电率相关, 30 Hz持续刺激比递减模式(30 Hz下降到15 Hz)作用力持久[15]。
Moritani等[16]研究表明20 Hz刺激频率比50 Hz或 80 Hz对诱导肌肉肥大更有效。一般认为,神经肌肉电刺激频率应设定在10-50 Hz范围内,上肢理想的刺激频率为12-16 Hz,下肢理想的刺激频率为18-25 Hz[17]。
2.2 神经肌肉电刺激在前交叉韧带重建后干预效果的评 价 国外早在1979年就将神经肌肉电刺激应用于前交叉韧带重建后早期康复。但研究普遍聚焦神经肌肉电刺激对股四头肌的影响。文献中罕见质疑神经肌肉电刺激在前交叉韧带重建术后康复中疗效,过往研究关注焦点在于神经肌肉电刺激的临床作用和优势[18]。
2.2.1 CT检查神经肌肉电刺激对前交叉韧带重建后患者肌肉横截面积的影响 Arvidsson等[19]对38位内侧1/3髌腱重建前交叉韧带患者在重建后进行电刺激对照实验,在重建前及重建后40-45 d进行计算机断层扫描(CT)检查,结果显示电刺激组男性腘绳肌横截面积明显降低。女性对照组股四头肌横截面积降低31.4%,电刺激组降低15.6%。活检结果显示电刺激组女性肌纤维面积下降5.4%,对照组女性及所有男性肌纤维降低30%-40%。
Wigerstad等[20]对26位内侧1/3髌腱重建前交叉韧带患者在术后固定期进行电刺激对照实验,重建后6周进行CT评价。结果显示CT检查电刺激组横截面积降低小于对照组。可见电刺激能有效缓解前交叉韧带重建后肌肉萎缩。
2.2.2 神经肌肉电刺激对前交叉韧带重建后患者酶活性的影响 Eriksson和Haggmark[21]采用常规康复等长训练基础上电刺激干预前交叉韧带重建后患者4周。结果显示对比等长训练组,电刺激组股四头肌琥珀酸脱氢酶活性增强。
Arvidsson等[19]对38位内侧1/3髌腱重建前交叉韧带患者在重建后进行电刺激对照实验,在重建前及重建后40-45 d进行组织活检,结果显示与术前相比柠檬酸合成酶在重建后第1周即开始降低,组间无区别。磷酸果糖激酶术后均下降,组间无区别。比较前交叉韧带重建前至重建后6周固定期,电刺激组男性磷酸果糖激酶显著下降。
Wigerstad等[20]对26位内侧1/3髌腱重建前交叉韧带患者在重建后固定期进行电刺激对照实验,重建后6周进行肌肉活检评价。结果显示前交叉韧带重建前柠檬酸合成酶组间无显著区别。重建后固定期手术腿柠檬酸合成酶均显著下降。重建后仅对照组三磷酸脱氢酶显著下降,两组有显著区别。前交叉韧带重建后电刺激治疗对肌肉酶活性也能产生积极影响。
2.2.3 等长及等速肌力测试分析神经肌肉电刺激对前交叉韧带重建术后患者股四头肌肌力的影响 Sisk等[22]对22位前交叉韧带重建后患者进行电刺激随机对照实验,研究电刺激对患者股四头肌等长收缩力量的影响。电刺激干预6周,在前交叉韧带重建后第7,8,9周进行股四头肌等长肌力测试,结果显示两组之间无显著差异。
Wigerstad等[20]对26位内侧1/3髌腱重建前交叉韧带患者在重建后固定期进行电刺激对照实验,重建后6周进行等长肌力测试,结果显示与电刺激组相比,对照组股四头肌等长肌力明显下降。
Delitto等[23]对20位重建前交叉韧带重建后患者在等长收缩的基础上进行随机分组电刺激对照实验6周。结果显示电刺激组与对照组相比等长肌力显著增加。
Snyder等[24]对比了110位各种术式重建前交叉韧带重建后患者高强度电刺激、低强度电刺激以及高强度自主收缩练习的影响。结果显示高强度电刺激组股四头肌等长肌力显著优于低强度电刺激组和自主收缩组。
Paternostro等[25]对49位前交叉韧带重建术后患者进行电刺激对照实验。分别在第6,12,52周进行等长和等速肌力测试,所有结果均无显著性差异。
Rebai等[26]对10位前交叉韧带重建后患者在常规康复基础上分别对股四头肌进行80 Hz和20 Hz的电刺激干预,共计12周。重建后12周等速肌力结果显示,20 Hz组患侧肌力恢复较好,但未达到术前水平,2组无显著性差异。
Hasegawa等[27]对20位前交叉韧带急性损伤自体腘绳肌重建后患者进行神经肌肉电刺激对照试验。受试随机分为常规康复基础上电刺激组和常规康复组,前交叉韧带重建前、重建后4周和重建后3个月分别进行等长、等速肌力测试。结果显示4周后电刺激组伸膝力量下降程度明显低于对照组,重建后3个月伸膝肌力恢复效果优于对照组。
仅1项研究对比使用不同刺激强度对等速肌力的影响,大部分研究结果显示重建术后电刺激能有效提高等速肌力。
2.2.4 其他影响 Snyder等[24]对10位前交叉韧带重建后患者在重建后3-6周进行实验,在等长收缩基础上进行电刺激干预。步态和KT-1000结果显示,电刺激组步态较好,KT-1000结果两组无显著差异。
Ross等[28]对20位自体髌腱前交叉韧带重建后患者进行神经肌肉电刺激与闭链运动对照试验。两组在康复训练的基础上分别进行电刺激和闭链运动干预,重建后6周进行KT-1000、单次下蹲试验、侧步试验和前伸试验评价。结果显示电刺激组单侧下蹲屈曲角度增加6.07°,侧步测试中平均多3.3步,差异显著,KT-1000两组无显著差异。
Ross认为神经肌肉电刺激提高下肢性能优于闭链运动。
Fitzgerald等[29]将48位前交叉韧带重建后患者进行电刺激随机对照试验。在重建后12周和16周进行日常生活能力(Activity of Daily Living Scale,ADL)量表和膝关节疼痛评分(0-10分)评价。结果显示电刺激组在术后12周电刺激组ADL量表评分较高,膝关节疼痛评分两组无显著性差异。
Hasegawa等
[27]对20位前交叉韧带急性损伤自体腘绳肌重建后患者进行神经肌肉电刺激对照试验。受试随机分为常规康复基础上电刺激组和常规康复组,重建前、重建后4周和重建后3个月分别进行超声以及Lysholm量表评分。结果显示电刺激组股外侧肌群和腓肠肌肌肉厚度显著增加,Lysholm量表统计结果两组间无显著区别。
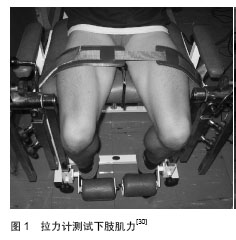
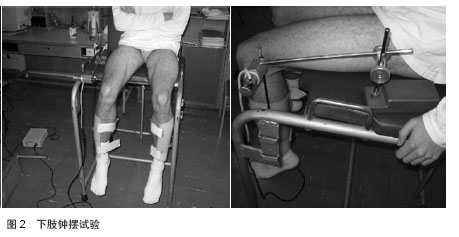
Takahashi等[30]对80位男性前交叉韧带重建术后足球运动员在常规康复基础上对股四头肌进行神经肌肉电刺激干预试验1个月。分别在重建后1个月和重建后3个月后使用便携拉力计测试肌力(见图1,2),进行圆周测试和摆锤测试,结果均无显著性差异。
但Takahashi等[30]认为神经肌肉电刺激对股四头肌肌力康复有益。其他评价方式也从一定程度上反映了电刺激在前交叉韧带术后康复中的积极作用。
国内文献罕见神经肌肉电刺激临床应用的报道。原因可能有以下两点:①专业人士对神经肌肉电刺激的认识不足。②国产神经肌肉电刺激性能的稳定性和可操作性。